In some remote locations, it’s easier and more economical to pump water out of a ground bore than it is to connect to a water supply network. Find out what’s involved, and what sorts of issues need to be considered.

What is bore water?
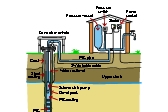
Bore water is ground water which accumulates in aquifers ( a natural underground storage formation) as a result of water from rain and rivers seeping through layers of soil and rock. A water bore is a way of gaining access to these groundwater sources, and is a popular choice for those who don’t have reliable access to water from other sources like the mains supply, regular rainfall or a nearby river.
Water is normally accessed via a deep hole bored into the earth (called a ‘borehole’), and drawn out of aquifers using a water pump. A bore typically consists of a pipe set vertically into the earth, providing direct access to water in the aquifer. At the bottom of the pipe is what’s known as a well screen – this is the part that allows in the water, while holding the walls of the bore in place and filtering out any sand or clay (like a tube with small holes in it).
Bore water is often ‘hard’ – that is, it often has a high mineral content. While hard water itself isn’t necessarily harmful to your health, it can leave mineral deposits on the insides of pipes, in hot water systems and wreak havoc on other parts of your plumbing system. Hard bore water can be softened using commercially available water softening appliances.
Deep bore water
Deep bore water is found in confined aquifers, buried deep beneath many metres of soils and clays. These soils and clays act as a kind of filter against microbial contamination, and as a result the quality of water in deep or confined aquifers is generally pretty good. The quality of this deep bore water will be retained if the bore is properly constructed, protected from entry of surface water and generally kept well maintained.
Unfortunately, water in these aquifers can also contain high concentrations of naturally occurring hazardous chemicals too. Before using a deep bore, you should obtain a proper chemical analysis of the water to make sure you know exactly what’s in it and whether or not it’s safe for you to drink without certain kinds of treatment.
Shallow bore water
Shallow bores are in unconfined aquifers, which are those not protected by thick layers of soils and clays. These types of bore are prone to both chemical and microbiological contamination. Because of this, shallow bores are generally not recommended as a suitable source of drinking water, especially in urban areas.
Bore location and installation
The location of a bore can affect the quality of the water that comes out of it. You should consider the kinds of things that might pollute the water, and in particular how close it will be to the septic tank if you have one. Waste disposal areas are another thing that can affect the quality of bore water if they’re too close. A bore at the bottom of a gully where surface runoff could submerge it, or in the path of effluent from factories or stormwater drains aren’t suitable either.
If you are thinking of creating any sort of bore, you must obtain a permit and it must be installed by a licensed water bore driller.
Is bore water safe to drink?
Bore water can be used as drinking water, provided that it’s not contaminated by microbial or chemical impurities. It can also be used for irrigation purposes and livestock watering, however this is dependent on the quality of the water being extracted.
For more information about water quality and making sure it’s safe for various uses, refer to the Australian Drinking Water Guidelines and the Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality.
Common contaminants
Some bore water contains chemical and microbiological hazards that are potentially harmful to your health. These hazards can either occur naturally, or be the result of contamination somewhere along the line. Some of the contaminants you might find in bore water include:
- E.coli (as an indicator of faecal contamination)
- Arsenic
- Fluoride
- Nitrate
Bore waters impacted by human and agricultural activities in particular can contain high concentrations of nitrate. If you have a bore, it’s your responsibility to monitor the water quality for any undesirable changes and conduct regular commercial testing.





